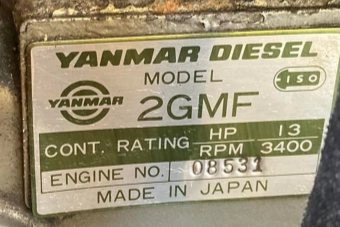
There are four main model variants of the Yanmar 2GM in circulation. The “F” indicates indirect (freshwater) cooling. Yanmar upgraded from the 2GM and 2GMF in 1983 after approximately four years of production. The difference between the 2GM/2GMF (13hp) and the 2GM20/2GM20F (18hp) is in the displacement and maximum operating rpm of the engine. Notably, the sump plug was eliminated in the redesigned engine. Lubricating oil must now be removed via the dipstick hole using a vacuum pump. The redesigned engines were produced until 2005. See the table below for exact specs.
| Model | 2GM/ 2GMF | 2GM20/ 2GM20F |
|---|---|---|
| Years of production | 1980 - 1983 | 1983 - 2005 |
| Idle (no-load) speed (rpm) | 850 | 850 |
| Full load speed (rpm) | 3750 | 3825 |
| Fuel Injection Timing | 25° before TDC | 15° before TDC |
| Valve Clearance | 0.2 m (0.008 in.) | 0.2 m (0.008 in.) |
| Oil Capacity | 2 litres / 2.1 qt | 2 litres / 2.1 qt |
| Num of Cylinders | 2 | 2 |
| Displacement | 586 cc / 35.7 cu. in. | 636 cc / 38.8 cu. in. |
| Horsepower | 13 hp @ 3400 rpm | 16 hp @ 3400 rpm |
| Gearbox | KM2A | KM2C or KM2P |
| Gearbox Ratio | 2.21, 2.62 or 3.22 | 2.21, 2.62 or 3.22 |

How is it cooled?
Is your engine raw-water or fresh-water cooled? Note that the raw-water cooled engines have no heat exchanger – the large unit on the top with “YANMAR” embossed on it. In addition, if you look very carefully, you can see the two anode locations on the raw-water cooled engine.



How heavy is a Yanmar 2GM20 Diesel Engine?
The different models of the Yanmar 2GM20 weigh between 106 kg (234 lbs) and 129 kg (278 lbs). The raw-water cooled 2GM20 with the KM2P transmission had a dry weight of 106Kg (234 lbs). The dry weight of the engine equipped with freshwater cooling (2GM20F) and the KM2P transmission is 114 kg (251 lbs). When the engine is equipped with the angled V-drive gear option (2GM20FV) complete with KM3V transmission, the dry weight increases to 129 kg (278 lbs). Lubricating oil, coolant and any alternator upgrades will add to this weight.

Do you have a Japanese or a European Engine?
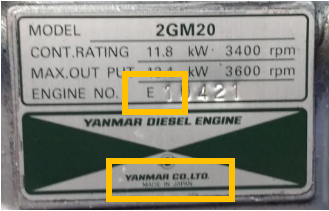
The Yanmar 2GM20 raw-water cooled engine was available in two main variants. One was manufactured in Japan and is known as the 2GM20 and the other was partly assembled in Europe, in the Netherlands from the mid-80s, and is known as the 2GM20-YEU. The YEU variant has an “E” at the beginning of the serial number although notice that the label still has “made in Japan” at the base (both shown in the image). The YEU varient is identical to the Japanese engines in most ways but the raw water pump is an area where the two engines differ. So if you are changing the impeller, be sure to pick the correct guide for your engine.

Components of the 2GM Engines
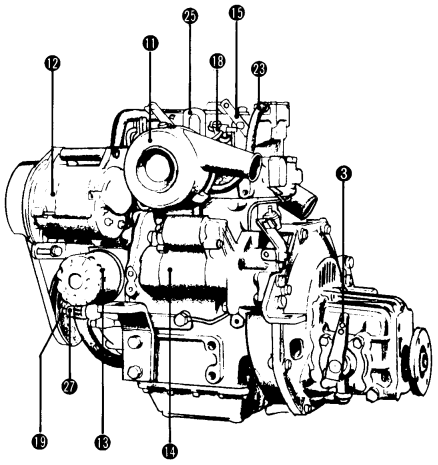
- Reduction & reversing gear
- Output shaft coupling
- Clutch control lever
- Installation foot
- Engine oil dipstick
- Clutch/gear oil dipstick
- Cooling water pump
- Fuel feed pump
- Mixing elbow
- Air intake silencer
- Alternator
- Engine oil filter
- Starter motor
- Oil pressure sender
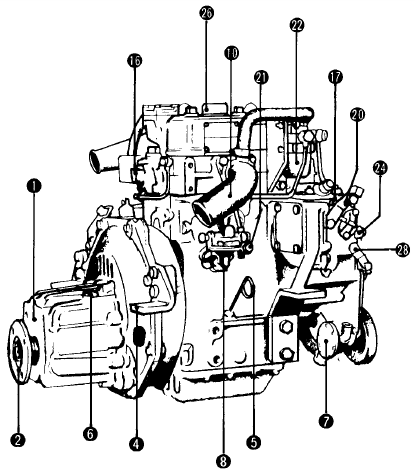
- Decompression lever
- Anti-corrosion zinc
- Fuel injection pump
- Fuel injection valve
- Crankshaft V-pulley
- Speed control lever
- Cooling water drain cock (Cylinder block & exhaust manifold)
- Fuel filter
- Breather pipe
- Fuel injection limiter
- Engine lift plate
- Engine oil supply port
- Engine stop device


TOP TIP: Use this handy printout to record all the important details about your Yanmar engine and then file it away safely at home for future reference.
Upgrade jobs for your Yanmar 2GM
- Adding a hour meter to your Yanmar GM series engine
- Adding a relay to the starter circuit to fix intermittant starting issue
Maintenance jobs for your Yanmar 2GM
- Changing the primary fuel filter on your marine diesel installation
- Checking the starter motor drive belt on your Yanmar 2GM20
- Removal and inspection of the air filter on the 2GM20
- Removal and inspection of the exhaust mixing elbow on the 2GM20
- Descaling the raw water coolant channels in your 2GM (Raw water cooled engines only)
- Descaling the heat exchanger in your 2GM (Fresh water cooled engines only)
Winterising jobs for your Yanmar 2GM
Before haul-out:
- Yanmar 2GM20 engine oil and filter change – see our Yanmar Oil change “hacks” here
After haul-out:
- Flushing salt-water from the Yanmar 2GM20 and introducing anti-freeze
- Clean and winterise the raw-water filter
Before launch:
- Stern gear: Grease your lip seal or refill the greaser on your stuffing box
- Changing the Secondary Fuel filter on the Yanmar 2GM20
- Inspecting the anodes on your Yanmar 2GM20 (Raw water cooled engines only)
- Removing and testing the thermostat on your Yanmar 2GM
- Removing and inspecting the air intake filter/silencer on the Yanmar 2GM
After launch:

Video Clip: Click to watch a quick video of a 2GM running


Having difficulty starting your 2GM?
Some problems are common between lots of diesel engines – see our checklist of the most common faults. If you’re seeing smoke from your exhaust, read this. But every variant of engine has its own idiosyncratic “personality” so we’ve gathered together a list of the common faults for the 2GM.
If you are experiencing problems starting a 2GM, and you have eliminated fuel supply problems then it might be worth considering compression. The 2GM has a pre-combustion chamber under the fuel injector but no pre-heating, so having sufficient compression to achieve combustion is important. The compression can be checked by removing the injector and using a compression tester.
It’s worth noting that it is possible to bend the connecting rod(s) by having water in the combustion space which could have been caused by a failing exhaust elbow. Bent rods will reduce the compression ratio of the engine. Yanmar uses con-rods that will bend so that no more serious damage occurs in the event of hydraulicing. This can be checked by measuring the ‘top clearance’ between the piston at TDC (top dead centre) and the cylinder head.
Here’s how to do it:
- Remove both the injector and the pre-combustion chamber.
- Lower the piston.
- Insert some 1.2mm diameter fuse wire into the space and then crush the wire by raising the piston to TDC by hand.
- Lower the piston, remove the wire and measure the thickness of the crushed part. The top clearance should be 0.68-0.88mm.
Other Common troubleshooting issues


A smart skipper learns from the lessons of others.
In our Yanmar GM Series Almanac section, we have a series of previous questions and queries from Yanmar GM owners along with answers. Many of these have been adapted from discussions on the “Yanmar Marine Engine Owner’s Group – Repair and Discussion” Facebook group which is a fantastic resource for getting help.
- White Smoke & Black Water from a Yanmar 2GM20
- KM2P Transmission Oil level question – please can someone help?
- Yanmar 1GM won’t go over 2700 RPM
- This Yanmar 2GM20 only started with one decompression lever engaged
Do you want to get future Yanmar GM Series Almanac articles straight to your inbox? Sign up to our Yanmar GM Series Owners’ Group today and we’ll make sure that you’re first to see them. And we definitely won’t share your email address with anyone else.

DOWNLOAD: Click here to download the original Yanmar 2GM20 sales brochure
DOWNLOAD: Click here to download the original Yanmar 2GM20F sales brochure

